With the rapid development of automobile, aerospace, aviation, military, information technology and machinery manufacturing, modern machining is increasingly pursuing the goal of “high precision, high efficiency, high reliability and specializationâ€, which requires the tool industry. It is even more important to develop high-quality materials for the manufacture of tools for tools that offer high cutting performance.
Powder metallurgy high-speed steel was developed in the late 1960s and put into use in the 1970s. The special and advanced smelting method of powder metallurgy high-speed steel is an innovation of high-speed steel smelting, which creates a new steel grade with properties between cemented carbide and ordinary high-speed steel, which makes the tooling materials of the machinery manufacturing industry new. Breakthrough. As a new steel with excellent performance, powder metallurgy high-speed steel is gradually recognized and accepted by people, playing an increasingly important role in the mechanical processing industry.
1. Smelting characteristics of powder metallurgy high speed steel
Compared with the smelting of ordinary high-speed steel, the smelting of powder metallurgy high-speed steel has its particularity and advancement. After ordinary high-speed steel is smelted by electric arc furnace or induction melting furnace, the molten steel is directly poured into steel ingot, and then processed into steel by forging and rolling. However, since the molten steel is poured into steel ingot, the solidification speed is very slow, from the molten steel. A large amount of metal carbides are precipitated to form fishbone-like Leysite and agglomerated coarse eutectic carbides, and carbide segregation is generated, which directly affects various mechanical properties of steel, especially steel toughness.
The smelting of powder metallurgy high-speed steel is different. The molten steel melted by the electric arc furnace or the induction melting furnace is not directly poured into steel ingot, but the molten steel liquid is sprayed into the high-pressure nitrogen stream through the nozzle, and the molten steel is rapidly fogged. Cooled into fine steel particles, the diameter of which is generally less than 1 mm. The steel powder thus prepared is put into a steel drum, and the steel drum is evacuated, so that the air between the steel powder in the barrel is vacuumed, and then the steel drum is welded, and then the steel in the steel drum is heated under high temperature and high pressure. The powder is pressed and formed to form a hot isostatic pressing sintering preparation process. This produces a powder metallurgy high speed with a density of almost 100%.
The steel billet is then forged and rolled into steel. Due to the powder metallurgy in the spray milling process, the molten steel cools very fast, avoiding many defects in the ordinary high-speed steel ingot process, and carbonizing in the atomized molten steel. The material does not have to grow and grow to form a mass, so the carbide particles are fine and uniform, generally 1 to 3 μm (the maximum size does not exceed 6 μm), which greatly improves the strength and toughness of the steel.
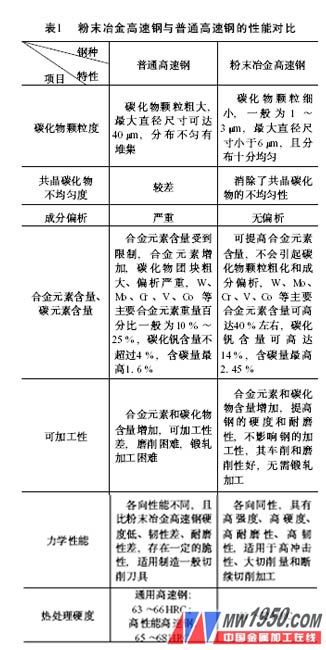
2. Properties and characteristics of powder metallurgy high speed steel
The special smelting method of powder metallurgy has superior performance and characteristics compared with ordinary high-speed steel (see Table 1).
Next page
Volumetric Water Meter,Rotary Piston Water Meter,Piston Water Meter,Ultrasonic Residential Water Meter
Shandong Chenshuo Meter Co., Ltd. , https://www.chenshuometer.com
