1 test
1.1 Methods and Instruments
The visual method is used to measure the cloud point of the plating solution. The process is: (1) Take a certain amount of solution containing the test agent, and heat it in the electric furnace until the solution becomes turbid; (2) Stop the heating and slowly cool down with stirring. The temperature immediately after clarification is the cloud point; (3) When it is necessary to observe the influence on the plating, use the Hull cell equipment to test the performance of the plating solution. Each data test 3 points, if the gap is larger, then retest.
1.2 Base Fluid Formula and Process Conditions
Potassium chloride (plating grade) 220g/L
Zinc chloride (plating grade) 80g/L
Boric acid (plating grade) 30g/L
Benzene* Acetone 0.4g/L
Pingping 0-15 4.0g/L
pH 5.0
Temperature 25°C
Current density 2.0A/dm2
2 Analysis of results
2.1 Effect of main salt concentration
The influence of the main salt concentration on the cloud point of the non-ionic surfactants mainly depends on the salt concentration and the valence of the ions. In general, the higher the salt concentration, the lower the cloud point; the higher the ionization valence of the constituent salts, the more the cloud point decreases. Table 1 shows the effect of potassium chloride and zinc chloride content on cloud point.
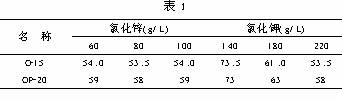
From the test results, it can be seen that with the increase of potassium chloride content, the cloud point of the plating solution decreases significantly, which is in line with the general rule, but the effect of zinc chloride on the cloud point is abnormal. The test results show that the zinc chloride content has almost no effect on the cloud point, which is far from the general theoretical rules (using distilled water, pipettes, volumetric flasks and other accurate weighing methods many times, repeated verification, the results are the same ). The real cause of this anomalous result needs further study.
2.2 Relationship with non-ionic surfactant concentration
The effects of nonionic surfactant concentration and cloud point were tested and the results are shown in Table 2.
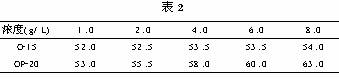
From Table 2, it can be seen that the concentration of the surfactant increases, the cloud point of the flat plus O-15 is slightly increased, and the increase of the OP-20 is more obvious. Taking into account the normal content of non-ionic surfactant in chloride galvanizing, only the concentration range in the table was determined, and other concentrations were not measured.
2.3 Relationship with Benzene* Acetone Concentration
Benzene*acetone is still the main brightener in chloride galvanizing. Benzene* acetone is insoluble in water, mainly dissolved by the solubilization of non-ionic surfactants, so the higher the benzyl* acetone content, the lower the cloud point of the nonionic surfactant should be. Table 3 shows the test results.
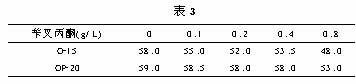
The test result of the benzyl* acetone content showed that the content increased and the cloud point decreased, which conformed to the general rule.
2.4 Relationship with auxiliary brighteners
The auxiliary brightener is an important component in chloride zinc plating. In this test, the commonly used main auxiliary brighteners (nicotinic acid, cinnamic acid, benzoic acid, and diffusing agent) were tested. The results are shown in Table 4.
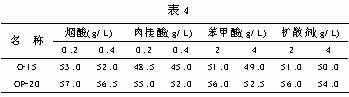
It can be seen from the above that benzoic acid and cinnamic acid have a greater influence on the cloud point, and with the increase of the content, the cloud point decreases more obviously. The weaker the auxiliary brightener acid (such as cinnamic acid), the more pronounced the cloud point decrease. This is because the organic acid in the galvanizing solution is a weak acid, the solubility is greatly affected by the pH value, the solubility in the weak acid chloride galvanizing solution is very low, and is mainly dissolved by the aid of the non-ionic surfactant. Therefore, when the temperature rises, the dissolving effect of the non-ionic surfactant on the organic weak acid is weakened, and the organic acid precipitates first and causes the solution to bleed. Actually, the turbid substance at this time is not a precipitate of a nonionic surfactant but a minute solid precipitate of weak acid.
2.5 Effect of Other Additives on Cloud Point
The effect of alkyl ether polyethylene glycol sulfate salt, alkyl ether polyethylene glycol sulfonate anionic surfactant and organic solubilizer on the cloud point was tested. The results are shown in Table 5.
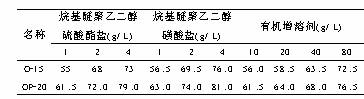
From the results, it can be seen that all three substances have a large effect, but there are too many anionic surfactant foams, and the anionic ether-polyethylene glycol sulfate type anionic surfactant is even more so. In addition, anionic surfactants have an adverse effect on high current density regions, affecting the current density upper limit. The organic solubilizer does not produce any foam, but also has an auxiliary complexation and buffering effect. The content range is also wide. The test solution has no adverse effect on the solution within a test range of 100 g/L. The higher the content, the higher the cloud point. The general rule in the test range is that the content increases by approximately 4.5 g/L, and the cloud point increases by 1°C. Organic cosolvents have a wide supply, low prices, and have considerable application value in chloride galvanizing.
2.6 relationship with the plating solution pH
Supplementary additives in the chloride galvanizing solution are components that must be added, and most are weak acids, which have a large effect on the cloud point. Therefore, when the relationship between the cloud point and the pH value was tested, different auxiliary brighteners were added and their contents were changed. The solution test results with the addition of diffusing agent and benzoic acid are shown in Table 6.
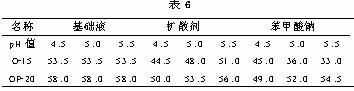
From the results, the pH value had no effect on the cloud point in the base fluid containing only the nonionic surfactant and benzyl*acetone, but when the auxiliary additive was included, the cloud point decreased significantly. These indicate that the pH value of the solution added with the auxiliary brightener has a greater influence on the cloud point. Similarly, weak acidic auxiliary additives such as nicotinic acid and cinnamic acid also have a greater impact on the cloud point.
3 Conclusion
The cloud point of non-ionic surfactants decreased with the increase of benzyl*acetone, auxiliary additives (sodium benzoate, diffusing agent, etc.), and increased with the increase of the main salt content of the solution, but the zinc chloride content had no effect; When the weak acid auxiliary additive is added, the cloud point decreases significantly with the decrease of the pH value, and increases significantly with the addition of alkyl benzene or alkyl alcohol polyglycol salt anionic surfactants and solubilizers; with nonionic surface activity The agent concentration increased slightly.
Starch Slurry Pump,Paper Making Starch Slurry Pump,Making Industry Lobe Pump,Starch Slurry Transfer Pump
NINGBO DURREX PUMPS CO.,LTD , https://www.durrexlobepump.com
