A company applies the nitrogen-based controlled atmosphere casting chain furnace automatic production line to the quenching and tempering process of GCr15 steel bearing rings. The quenching medium mainly uses N32 mechanical oil. With the increase of the size of the ferrule, there are sometimes problems such as severe unevenness and distortion of the quenching hardness. After modifying the N32 mechanical oil with the Y15T rapid quenching oil additive, the ferrule hardness is unevenly determined and effectively controlled. Quenching distortion.
The company's cast-chain furnace production line has been put into production and has accumulated more than 7000t of quenched workpieces. The product quality is controlled within the JB/T 1255—1 991 standard. The quenching medium is mainly N32 mechanical oil, and the N15 mechanical oil is partially supplemented in winter. Quenching media, in addition to strict control of moisture content, take other testing methods, and have not dealt with quenching quality problems for many years.
After 6 years of use, due to the aging of the old oil, the surface brightness of the workpiece is reduced after quenching. The soot is large during the production. The new N32 mechanical turbidity is replaced by the groove of the quenching oil tank of the casting chain furnace, and the thick-walled large-sized ferrule is found shortly afterwards. (Outer diameter>100mm, effective wall thickness>10mm) After quenching, some ferrules (about 5%~20%) are prone to uneven surface hardness and local hardness is unqualified. Grade 6 appears (JB/T 1255-1991 The second level map) above quenched tissue.
On the end face of the part, the metallographic structure of the hardness-qualified area is grade 2, the amount of residual carbide is suitable, but the particles are coarse; the area of ​​unqualified hardness is mainly grade 6 and grade 8, and the shape of troostite is block-shaped, block-shaped Residual carbide particles are visible in the middle of the body.
(1) Analysis of quality problems
1 The original tissue uniformity is poor. According to the investigation, during the above problem, the spheroidizing annealing temperature exceeds 820 °C, and the annealed structure is rated at grade 4 (JB/T 1255-1991 first level map). Although it is qualified, some of the carbides are coarse and not distributed. Both of them cause difficulty in adjusting the quenching process. For this reason, the annealing process was immediately corrected, but the previously produced annealed billet was difficult to rework.
2 Whether the quenching temperature is low. The preparation of the JB/T 1255-1991 standard shows that the quenching and tempering microstructures of the 6th and 8th grades show that the quenching temperature is low. Increasing the quenching heating temperature and the lengthening time can increase the carbon and chromium content in the austenite, homogenize the austenite composition, increase the grain size, improve the stability of the supercooled austenite during quenching, and inhibit the transformation of the pearlite type. Improve the hardenability of GCrl5 steel. Reduce the critical quenching speed.
Accordingly, the quenching heating temperature is increased by 8 to 10 ° C, and the total heating time is extended by 10 to 15 minutes for mass production test, and the problem of unsatisfactory hardness can be solved. However, many ferrules have a large difference in hardness between the two parts, up to 2HRC. In the quenched and tempered structure, a small amount of small quaternary humite is still found in the local area. At the same time, fine acicular martensite appears, and the quenching deformation is sharp. rise. The variation rate of the diameter variation increases from an average of less than 10% to more than 25%, and the mechanical properties of the parts are relatively deteriorated. This can be seen. In the case of poor uniformity of the original structure, simply raising the quenching heating temperature and time to solve the problem of unqualified hardness is not the best way.
3 Whether the furnace insulation performance, furnace temperature uniformity and furnace loading have an impact. After investigation, the amount of furnace loading exceeded the process specifications. The following specifications are used to check the uniformity of the furnace temperature: no-load, the set temperature of the I, II and III meters is 850 ° C and has reached the thermal stability state, using 5 armored thermocouples in the same cross section of the working space of the cast chain belt ( 590mm width × 100mm height) simultaneously measure the temperature at the top left, bottom left, middle, upper right, and lower right, from the feed vibration guide groove at the opening of the casting chain (feeding port) to the end of the casting chain (returning material) The average value of the cross-section furnace temperature over the length of 4750mm is shown in the figure below.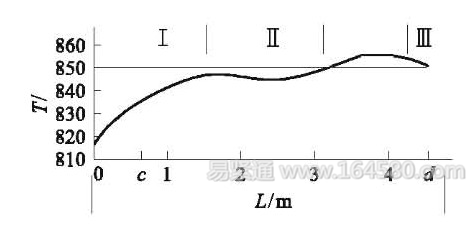
Schematic diagram of the mean temperature of each cross section in the cast chainThe I zone is close to the feed port and the feed port is open when the temperature is measured. The average temperature is 840 ° C, the average temperature of zone II is 846 ° C, and the average temperature of zone III is 854 ° C. The furnace temperature fluctuation is gentle throughout the heating length. Especially important for the continuous quenching furnace is the temperature difference at each point on the same cross section in the working space. The temperature difference between the points on the same cross section between point c and point d is within ±4 °C. The uniformity of the furnace temperature is good. The measured furnace shell temperature rise <40 °C. Therefore, it can be excluded that the performance of the furnace and the amount of furnace are factors that affect the uniform heating of austenitization.
4 quenching medium cooling capacity is insufficient. Due to the quality problem, the quenching oil tank of the casting chain furnace was replaced with the new N32 mechanical oil, and at the same time, the hardness of the same type of workpiece quenched by the old furnace in the box furnace was unqualified. From this analysis: on the one hand, the old oil (due to the inclusion of some N15 mechanical oil, its composition and aging degree is difficult to trace) cooling capacity is better than new oil; on the other hand, the workpiece is hooked or hand-held in the box furnace heating and quenching The wire quenching basket is shaken and cooled in the oil, and the relative movement between the workpiece and the quenching medium is uniform and sufficient, while the quenching oil tank of the casting chain furnace has a large volume, and has an automatic temperature control device for quenching oil, two gear oil pumps, and an oil mixer. The oil temperature in the quenching tank is evenly and stably controlled between 60 and 90 ° C, and the cycle is good. However, due to the large depth of the quenching tank, the oil flow formed by the operation of the oil mixer is not uniform to the surface of the quenched workpiece. The higher the speed of the oil mixer, the greater the quenching deformation of the workpiece, and the oil agitation zone formed by the operation of the gear oil pump and the oil mixer is mainly The upper and middle parts of the oil trough workpiece blanking guide groove, when the red hot workpiece falls vertically into the oil tank, immediately pass through the oil stirring zone and then stop on the slowly running lifting mesh belt at the lower part of the oil tank. The movement between the workpiece and the quenching oil is relatively slow. And some of the workpieces may overlap each other. At this time, if the cooling capacity of the quenching oil itself is insufficient, the local cooling rate of the workpiece is lower than the critical quenching speed, and the troostite transformation may be the main reason for the partial hardness failure after quenching of the partial ferrule.
Subsequent testing of the quenching and cooling characteristics of new and used oil samples using the ISO 9950 standard confirmed this analysis.
(2) Improvement of quenching medium and its effect. The company believes that N32 mechanical oil is used in the automatic production line thick-walled large-size ferrules when quenching the cooling capacity is insufficient, in view of the compact structure of the quenching oil tank is difficult to change, now N32 mechanical oil is still acceptable, decided to improve the cooling of quenching oil alone Experiment on characteristics.
After comparison test, the company selected the N32 mechanical oil in the tank by using the Y15T fast bright quenching oil-tantalum additive. After the modification, the quenching oil has a faster cooling rate, the maximum cooling rate is increased by 20 ° C / s, the vapor film phase time is shortened by nearly half, and the maximum cooling rate is increased by 50 ° C, which is beneficial to suppress the diffusion type transition of the quenched structure.
The improved quenching oil is quenched by a thick-walled large-size GCrl5 steel bearing ring with the same heating process as before the improvement. The hardness is all qualified, the hardness difference of the same part is within 1HRC, the microstructure of the quenched metallurgy is improved, the troostite disappears completely, and the ferrule is checked by pickling without crack, but the quenching deformation is still large.
After the test, the temperature is 2~5°C lower than the normal heating temperature, and the quenching oil tank mixer speed is reduced. The quenching hardness of the bearing ring is controlled at 64~65.5HRC, the metallographic structure is 2~3, and the level is 2 After the quenching of the outer diameter >100mm, the diameter variation of the ferrule is reduced to about 7%, and then the quenching workpiece is nearly 3000t. The maximum effective wall thickness of the GCr15 steel tapered roller bearing ferrule is 15mm, non-standard roller bearing. The maximum effective wall thickness of the ferrule is 23mm, and all the quality is qualified, which reduces the waste and repair loss. Since the mechanical oil of the groove N32 is still clean, the surface of the improved workpiece is bright and non-polluted after quenching, and the oil smoke is less during quenching, which improves the surface quality of the workpiece and the working environment of the workshop.According to the material of the part, the original structure, the quenching method, select the quenching medium with appropriate cooling characteristics, and regularly monitor and adjust the cooling characteristics, improve the cooling characteristics of the quenching medium within the allowable range, improve the hardness and uniformity of the parts after quenching, and expand the steel grade. The scope of use, and through the adjustment of the heating process to achieve the effect of reducing quenching deformation. Cooperating with the control atmosphere heating furnace can obtain the bright and clean appearance quality after quenching, reduce the volatilization of the soot, and is beneficial to the heat treatment and clean production.
Full thread studs are special grade bolts, represented by material grades. Material substitution for chemical equipment must be confirmed by design before it can be represented. Once, it was seen on site that Grade 4.5 hexagonal bolts were used instead of Grade 8.8 bolts
Fully Threaded Stud,B7 Full Thread Studs,Pressure Resistant Screws,High Strength Fully Threaded Studs
AM FASTENER , https://www.asmefastener.com
