I. Overview
The current production method of φ40mm low-chromium alloy grinding ball in our factory is metal-type one-eight-ball + silica sand riser forming process, which has achieved good application effect of saving more than 1 million yuan of grinding ball cost in the concentrator.
With the development of China's foundry technology, the advent and promotion of some new technologies have made our original metal casting advantages become inferior, and have not adapted to the requirements of market economy development. Compared with new technologies, the following technologies exist. Insufficient aspects:
(1) The metal type has high manufacturing cost and short service life.
(2) The inner runner is baked by high temperature for a long time, which is prone to thermal fatigue pitting, which seriously affects the appearance quality of the grinding ball.
(3) High production cost and long cycle.
(4) Workers have poor working environment and high labor intensity.
New process features: high casting precision; high product quality; simplified process, easy to operate; stable process, low product rejection rate. Therefore, replacing the current process with a new process has become a necessity to participate in market competition.
Second, the test process control
Chemical composition control
(1) Carbon control w C = 3.0% to 3.8%. Like chrome white cast iron, carbon content is an important factor affecting its performance. As the amount of carbon increases, the hardness and wear resistance increase, and the brittleness increases accordingly. If the amount of carbon is too low, it is difficult to obtain a grinding ball with no defects on the surface and inside. This test takes a higher carbon in order to effectively increase the amount of carbide. As the amount of carbide increases, the number of hardened phases in the structure increases, which is beneficial to increase the strength and hardness of the grinding ball.
(2) Silicon control w Si = 1.4% to 2.6%. Silicon is an element that strongly promotes graphitization. If it is too low, it tends to cause shrinkage and cracking. However, if it is too high, the carbide content will be too high, brittleness will increase, and casting properties will deteriorate. It is extremely advantageous to take higher silicon in this test, because silicon does not form carbide elements, and it dissolves into solid solution, thereby reducing the solubility of carbon in the solid solution, improving the activity of carbon, and ensuring the basic stability of the amount of carbide. And the base has been strengthened.
(3) Manganese control w Mn = 0.4% to 0.8%. It is used to promote the formation of pearlite and Leysite, and to refine pearlite to improve the strength and hardness of cast iron, but it is easy to cause segregation and austenite in the structure. The metallographic structure and various properties of this material are mainly independent of manganese, so the content is considered in the usual range.
(4) Chromium control w Cr = 1.5% to 2.7%. The addition of chromium in white cast iron not only changes the phase structure of the carbide, improves the hardness and wear resistance, but also changes the distribution of the matrix and carbide, so that the white cast iron has better mechanical properties. However, as chromium increases, the brittleness increases accordingly.
(5) Sulfur and phosphorus are considered to have the same harmful effects as ordinary white cast iron, that is, w S and w p are both <0.06%.
(6) Rare earth modification treatment control w RE residual <0.02%, can make M3C type carbides change from continuous network to broken network and isolated distribution, and make the Leysite type into a plate shape. The rare earth has a strong purifying effect on the molten iron, and the gas content is reduced, so that the non-metallic inclusions tend to be spheroidized, which is beneficial to the improvement of the impact fatigue performance.
(7) Molybdenum control w Mo = 0.2% to 0.3%. The main role in steel is to improve hardenability, refine grains, improve the morphology and distribution of carbides, and prevent temper brittleness. Simultaneous addition with chromium improves impact toughness.
2. Forming process
(1) Production of foam type Firstly, a six-ball foam type aluminum alloy mold (see Fig. 1) was designed, and then the metal mold was sent to a foam factory for mass foaming to produce a foam type.
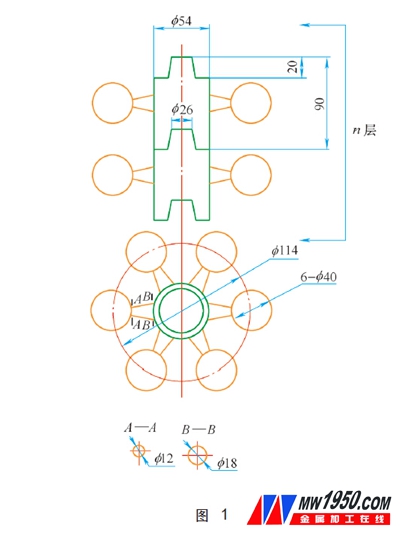
(2) Design of the slinging system First, the single foam type is connected in a string as shown in Fig. 1, and then connected together by criss-crossing foam strips (runners), and pouring is carried out by means of a top shot.
(3) Coating process 1 mixing process. First, dilute CMC (cellulose) with warm water, the ratio is CMC: water = 1:40, the parking time is not less than 4h, then pour the CMC aqueous solution into the mixing tank, stir for 1~2h; add white latex to stir 0.5~ 1h; then add high-quality bentonite, sodium carbonate, dextrin, stir for about 1h; finally add silica sand powder for 2~3h. Stir for 10 to 15 minutes before each use to make the ingredients uniform. 2 coating and drying process. It is combined with dip coating and brush coating. First, a large area coating was carried out by dip coating. The partially undip coated portion is further coated with a brush, and then dried, and the drying temperature is 30 to 40 °C. After drying, apply and brush for 3 to 4 times, and finally obtain a coating with a thickness of 1 to 1.5 mm.
(4) The buried tank is made of a bottom suction type negative pressure sand box with a diameter of 2720 mm and a height of 1500 mm. Silica sand having a particle size of 0.90 to 0.45 mm (20/40 mesh) was used as a molding material. The negative pressure value is controlled to 0.05 MPa, on the one hand, the amount of gaseous products in the pattern is greatly suppressed, and on the other hand, the sand type can establish a large positive pressure gradient from the pattern to the flask, accelerating the vaporization of the pattern and the decomposition of the liquid product. The speed of the coating and sand type. The pouring temperature is controlled at 1480 to 1500 ° C, and the pouring time is 140 s, and the pouring is smoothly achieved.
3. Melting process
It is smelted by medium frequency induction furnace. The medium frequency induction furnace is the most advanced and widely used melting equipment in the foundry industry. Due to its strong magnetic stirring effect, the molten steel can maximize the "temperature fluctuation", "concentration fluctuation" and "component fluctuation". Therefore, it provides the most favorable guarantee for obtaining high-quality molten steel with uniform and clean composition.
4. Heat treatment process
(1) After the water quenching process is completed, the ball is cooled to a dark red (600-700 ° C), hot-boxed, and the ball is quenched into water (water temperature is required to be 20-40 ° C) for heat treatment.
(2) After the air quenching process is completed, the ball is cooled to a dark red (600-700 ° C), hot-boxed, and the ball is exposed to the air for heat treatment.
(3) Design of quenching tank The quenching process is one of the most important aspects of this research work. Whether the performance indexes of the developed f40mm ball can meet the original design requirements, the key is to control this link, we design A water quenching tank was made to ensure the high quality of the development work.
(4) Selection of quenching cooling medium According to the cooling speed required by the heat treatment process and the strength, hardness and wear resistance required by the grinding ball, we have selected water and air as the quenching cooling medium based on the principle of reducing cost.
(5) Determination of the volume of the quenching tank The size of the quenching tank depends on the quantitative relationship between the quenching cooling medium and the grinding ball. According to the production experience, as long as the weight of the quenching cooling medium is 10 times the weight of the grinding ball, the process requirements can be fully satisfied.
Third, test results and analysis
Test result
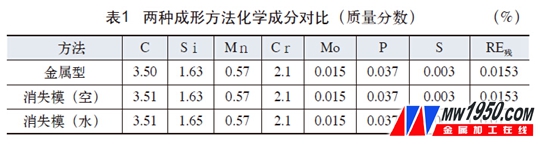
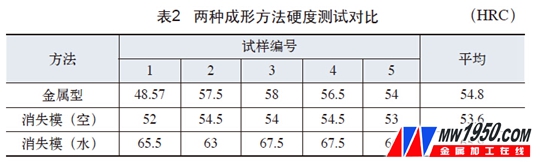
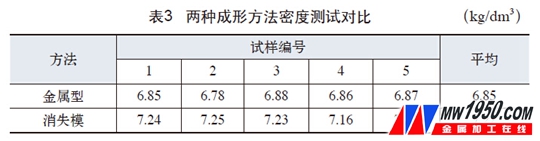
Through the control of process conditions, some φ40mm low-chromium alloy grinding balls are produced by the lost foam casting process. The surface of the casting ball is smooth and round, without fins, burrs, flesh and other defects. All performance indexes are better than metal-type production balls. See Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4).



2. Reason analysis
(1) It can be seen from Table 1 that the chemical composition of the φ40mm low-chromium alloy grinding ball is controlled within the control range regardless of the metal type or the lost foam. However, the carbon content of the lost mode is slightly higher, which is caused by the vaporization of the lost mode. The metal liquid is slightly carbonized, and as long as we consider this factor in the ingredients, we can control the ingredients to the required values.
(2) It can be seen from Table 2 that the voiding hardness value of the lost mode is slightly lower than the hardness value of the metal type, and the water hardness value of the lost mode is significantly higher than the hardness value of the metal type, because the effect of the air quenching is better than that of the metal. The type is slightly worse, and the water quenching effect is obviously better than that of the metal type.
(3) It can be seen from Table 3 that the density of the φ40mm low-chromium alloy grinding ball produced by the lost foam is also significantly higher than that of the low-chromium alloy grinding ball produced by the metal type, because the lost foam casting is more than the metal casting. It is more conducive to the temperature gradient conditions that cause the grinding ball to solidify sequentially, so the overall performance of the grinding ball is better than that of the metal production grinding ball.
(4) It can be seen from Fig. 2 to Fig. 4 that the φ40mm low chromium alloy grinding balls produced by the lost mode water quenching have better metallographic structure, carbide morphology and distribution than the use of lost foam and quenching and metal type. The reason for the production of low-chromium alloy grinding balls is that the comprehensive forming factors for the grinding balls produced by the lost-foam water quenching are better than those of the lost-formed air quenching and metal-type production. Therefore, the project finally uses the lost-form water. Quenching to produce φ40mm low chromium alloy grinding balls.
Fourth, industrial test
In this test, 1000kg of φ40mm low-chromium alloy grinding ball produced by the lost foam was put into use, and the comparison test was carried out in the wet mill of the large selection plant with the φ40mm low-chromium alloy grinding ball with metal type. After more than three months of practical application, I showed that The low chromium alloy grinding balls produced by the factory have the following remarkable features compared with the metal casting.
(1) The surface is smooth and free of casting defects such as sand, sand, pores and shrinkage.
(2) High intrinsic quality and good wear resistance.
(3) It can be applied under actual working conditions, and has good application effects such as no loss of roundness, no breakage, and low wear of the grinding ball.
(4) The service life is better than that of metal casting.
V. Conclusion
Reasonable material selection, advanced casting technology and reliable quality control measures are the key to producing high quality low chromium alloy grinding balls. With the promotion and application of the process, the quality of the grinding ball products of our factory will be comprehensively improved, the competitiveness of the market will be enhanced, and the social and economic benefits will be achieved.
About the author: Liu Li'an, Li Zhixiang, Shaanxi Huaxian Jinduicheng Molybdenum Industry Group Co., Ltd. Electromechanical repair plant.
Living Room,Accent Chair,Side Table,Tv Stand
PFALL , https://www.pfallfurniture.com
