Abstract: The formation process of the unsteady flow field of the friction stir welded onion ring and the influence of the process parameters on the onion ring were analyzed. The metal flow flowing into the cavity during the welding process (especially the metal flow opposite to the direction of rotation of the welding pin) The original flow field generated when the welding needle is not moving is destroyed, and a complex vortex flow is formed, and the unevenness is exhibited in the longitudinal direction, and the onion-like morphology is finally formed after the superposition. The experiment shows that the size of the stirring tool and the welding speed are affected. The main factor of onion round shape.
Key words: friction stir welding; onion ring; unsteady flow field
Friction stir welding is a new type of solid phase joining process, which provides a new way for the effective connection of aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy and other lightweight high-strength materials with poor fusion weldability. Friction stir welding has a refined forged structure, No weld defects such as porosity, cracks and element burning, and the weld quality is highly consistent; it can be applied to a variety of joint forms; the connection process is simple. It has been widely used in aerospace, shipbuilding, machinery, automobile manufacturing and other fields.
The onion ring is the most important feature of the friction stir welded joint. It is a joint shape formed by complex flow laws under specific process parameters. This area is affected by thermal cycling and mechanical interaction. High temperature, large strain rate and strain have undergone strong plastic deformation. The formation of relatively dense microstructure by dynamic recrystallization has a great influence on the welding properties of the material. Therefore, the formation process and influencing factors of onion rings are studied. It is of great significance to optimize the welding process and improve the welding quality.
1 Formation process of unsteady flow field of onion rings
During the friction stir welding process, the plastic softening layer is formed by frictional heat between the shoulder and the weld, and the heat input exhibits a gradient effect, and has a large strain and high in a portion close to the shoulder. The strain rate, under the action of the stirring head, undergoes dynamic recrystallization, forming fine equiaxed dynamic crystal grains, and the grain boundary is a large angular grain boundary. The weld nugget area of ​​the L F2 aluminum alloy friction stir welded joint is shown in Fig. 1. The welding process parameters are the speed n = 1500 r / min, the welding speed v = 90 mm / min. At the same time in the welding area due to the continuous input of heat, the mechanical action of the mixing head caused the grain boundary migration, the migration between the grain boundaries And the plastic flow causes the new grains to be chain-like nucleation and grow up, and the formed grain layer expands in the longitudinal direction to form a bundle-shaped grain zone. At this time, the plastic metal exhibits a characteristic of viscous flow.
Key words: friction stir welding; onion ring; unsteady flow field
Friction stir welding is a new type of solid phase joining process, which provides a new way for the effective connection of aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy and other lightweight high-strength materials with poor fusion weldability. Friction stir welding has a refined forged structure, No weld defects such as porosity, cracks and element burning, and the weld quality is highly consistent; it can be applied to a variety of joint forms; the connection process is simple. It has been widely used in aerospace, shipbuilding, machinery, automobile manufacturing and other fields.
The onion ring is the most important feature of the friction stir welded joint. It is a joint shape formed by complex flow laws under specific process parameters. This area is affected by thermal cycling and mechanical interaction. High temperature, large strain rate and strain have undergone strong plastic deformation. The formation of relatively dense microstructure by dynamic recrystallization has a great influence on the welding properties of the material. Therefore, the formation process and influencing factors of onion rings are studied. It is of great significance to optimize the welding process and improve the welding quality.
1 Formation process of unsteady flow field of onion rings
During the friction stir welding process, the plastic softening layer is formed by frictional heat between the shoulder and the weld, and the heat input exhibits a gradient effect, and has a large strain and high in a portion close to the shoulder. The strain rate, under the action of the stirring head, undergoes dynamic recrystallization, forming fine equiaxed dynamic crystal grains, and the grain boundary is a large angular grain boundary. The weld nugget area of ​​the L F2 aluminum alloy friction stir welded joint is shown in Fig. 1. The welding process parameters are the speed n = 1500 r / min, the welding speed v = 90 mm / min. At the same time in the welding area due to the continuous input of heat, the mechanical action of the mixing head caused the grain boundary migration, the migration between the grain boundaries And the plastic flow causes the new grains to be chain-like nucleation and grow up, and the formed grain layer expands in the longitudinal direction to form a bundle-shaped grain zone. At this time, the plastic metal exhibits a characteristic of viscous flow.

The onion ring is an important feature of the friction stir welded joint. The onion circular shape of the LD30 aluminum alloy friction stir welded joint is shown in Fig. 2. In this area, the material undergoes high temperature and severe deformation, and is unstable. The form of the flow field is expanded. How is this unsteady flow field formed? This can be roughly analyzed from two stages, namely inserting the to-be-welded part into the mixing head and applying a certain axial pressure. The first stage is the original flow field formed under the action, at which time the stirring head has not started to move along the weld; the second stage is the metal flow field of the mixing head filling the cavity during the running, interacting with the original flow field and Produce a superposition effect to form a new unstable flow field.

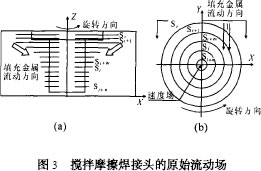
The original flow field of the friction stir welded joint is shown in Fig. 3. Fig. 3 (a) is an approximate velocity gradient of the X-Z in-plane metal flow field. When the X-Y plane is not welded, or the stirring head In the early stage of the start of the travel, the velocity gradient of the surrounding area of ​​the stirring head can be seen from Fig. 3 (b). There is a velocity gradient between the different plastic softening layers, the metal fluid velocity gradient in the shoulder region and the metal fluid velocity in the stirring head region. The gradient is different. The velocity gradient is transmitted to the Si + 1 layer by the shear stress at the interface of the grain layer near the Si layer, while the velocity gradient of the Sj layer metal fluid in the agitating needle region is similar to the bottom of the material, but it is worth Note that the metal fluid velocity gradient generated by the stirring head region and the metal fluid velocity gradient in the shoulder region form a superimposed flow field. This flow field causes strong plastic deformation of the crystal grains under the action of mechanical agitation. The strain rate is greater than 102, and the strain decreases rapidly with the distance from the center line of the weld. This is because the mechanical action is weakened as the distance increases, and the interaction between the grains is mainly dependent on the shear between the grains. Use, but this ideal original flow field is unstable or temporary. When connecting in the Y direction (ie, the welding direction), the metal in the forward direction will move backwards under the action of extrusion to form another non- The stable flow field interacts with the pre-applied ideal stable field, which leads to the inhomogeneity in the dynamic recrystallization process of the welded joint. That is, a vortex-like unstable flow field is formed, and the obtained onion ring diagram is obtained. It can be seen that the morphology of the joint is closely related to the inhomogeneity of this dynamic recrystallization. During the formation of recrystallization evolution, although dislocation plays an important role in it, for the sample, Violent continuous plastic deformation is only difficult to explain from this point of view, since the agitation process is achieved by a rotating welding pin, not only by grain boundary slip (and rotation), but also by intense pure shearing. process.
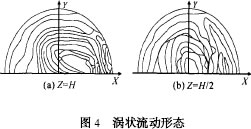
Due to the high-speed rotation of the stirring head, the metal in front of the stirring needle also enters a plastic state. According to the minimum resistance theorem, during the forward movement of the stirring head, this part of the metal will flow to the rear to fill the cavity area, and the flow generated in this part of the metal Under the action of the velocity field, the originally established flow field is destroyed, and the flow velocity field of the X-Y plane changes, forming a flow field as shown in Fig. 3 (b). From this flow field, it can be seen that the cavity is filled. This metal flow field has a great influence on the resulting unsteady flow field. In particular, the metal flow at the right side of the Y-Z surface causes the metal flow along the direction of rotation of the stirring head to be blocked, and the Y-Z side enters the left side. The metal of the cavity has little effect on the unsteady flow field, which coincides with a large offset of the root of the onion ring relative to the center plane (Y-Z plane), in addition to this metal pair flowing into the cavity The metal blocking action γ along the direction of rotation of the stirring head also occurs at the root of the stirring needle or the onion portion of the onion ring, causing the onion portion of the onion ring to partially offset from the center surface, but due to the inflow into the cavity Metal in the thickness direction The velocity gradient is relatively large. This offset is not very obvious. Figure 4 shows the vortex flow pattern of the X-Y plane along the thickness direction Z = H, Z = H/ 2. The onion is affected by heat and Where the most mechanical agitation occurs, this part of the metal flows in a spiral direction along the Y-axis until the end of the joining process.
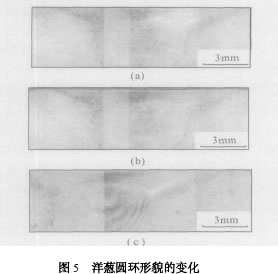
2 Factors affecting the unstable flow field of the onion ring <br> So what are the factors related to the shape of the onion circle formed by this unsteady flow place? For this purpose, the friction stir welding is connected using different process parameters. Different process parameters are used to explore the effect on this unsteady flow field. The LD2 aluminum alloy is frictionally connected under different process parameters, because the heat input power is mainly related to the rotation speed and the pressure between the shoulder and the workpiece. The rotation speed is 1 500 r/min, the welding speed is 250mm/min, 350 mm/min and 500 mm/min respectively. Corresponding to different process parameters, the morphology of the onion rings in the weld nugget area is also different. Figure 5 shows The morphology of the onion ring under the welding parameters shows that the annular shape of the onion ring is less and less obvious with the increase of the welding speed. KN Krishnan preliminary research on the friction stir welding head "onion ring" The analysis indicates that it is related to the geometry and process parameters of the weld head. Since both of them affect the movement of the plastic fluid, the generation of the ring depends on the movement of the plastic fluid; the center of the ring is dense and sparse to the periphery; The gap between the ring and the welding tool is equal to each turn [7]. When the rotation speed exceeds a certain range, the onion ring is not observed. This may be because the increase of the rotational speed causes the heat input power to increase greatly, resulting in the weld nugget area. The flow has undergone major changes, and research work in this area is being carried out in-depth research using experimental methods and simulation methods at home and abroad.
When the friction stir connection is carried out, the stirring needle continuously stirs and extrudes the material, the material undergoes great deformation, the strain amount and the strain rate are extremely high, and the crystal grains undergo repeated recrystallization to satisfy the plastic flow required for the material. Condition, the continuity of this plastic flow pattern has a great relationship with the rotation speed. As the rotation speed increases, the metal flow has better stability and continuity. With other process parameters unchanged, As the welding speed increases, the heat input decreases, and the dynamic recrystallization driving force changes accordingly, which causes the viscous effect between the metal softening layers in the advancing direction of the stirring needle to be strengthened, and the driving force for dynamic recrystallization of the onion portion of the onion ring decreases. Faster, making the expansion of the metal along the Y direction more and more difficult, the metal's flow transfer ability is reduced, the shape of the onion ring changes, and the spacing between the ring and the ring is getting larger and larger. The results observed by KN Krishnan are consistent.
It can be seen that the welding speed has a great influence on the flow field and the final shape during the formation of the onion ring. In addition, the different agitating needle shapes have different action forms on the flow field of the plastic material, such as a spiral shape. Compared with the cylindrical welding pin, the former has not only agitating and squeezing during the joining process, but also causes the material to produce a downward spiral flow field, which has a great influence on the final morphology and texture of the joint. Therefore, the influence of the shape and size of the welding tool can not be ignored. In addition, the shape of the onion ring onion is closely related to the size of the agitator shoulder. This effect is mainly reflected in the area of ​​the surface below 1 / 3 plate thickness, because this area The flow field is mainly agitated by the shoulder of the mixing head.
3 Conclusions <br> The metal flow particles in the plastic softening zone flow in a vortex-like unsteady flow field due to the constant flow of velocity and direction. The joint structure formed during the connection process is asymmetric, but basically remains. The microstructure of the joint with gradient characteristics. When connecting, the flow field formed by the cavity left behind the plastic fluid near the end face of the stirring head interacts with the flow field along the direction of the stirring needle, and this interaction is along the thickness. The direction is rapidly diminished, causing the onion-like morphology (including the onion to the root) to shift from the center plane, and the degree of this shift is more pronounced from the onion to the root.
The change of the eddy current unsteady flow field determines the onion morphology of the joint. The main factors affecting the vortex unsteady flow field are the welding speed and the depth of the shoulder pressed into the workpiece (also a form of axial pressure transfer). The shape and size of the welding tool can not be ignored.
3M Measuring Tape,Waterproof Tape Measure,Stainless Steel Tape Measure,Plastic Tape Measure
SHANGQIU CHAOYUE MEASURING TOOLS CO., LTD , https://www.calibrateds.com
