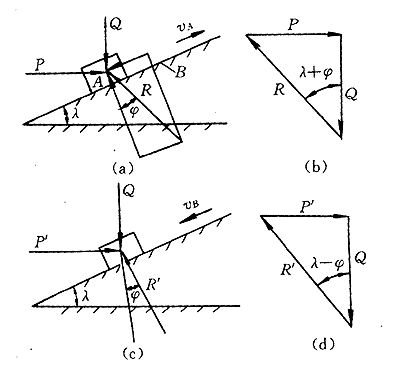
1 Characteristics of the beveled slider mechanismAs shown in Fig. 1a, the slider A is placed on a slope having a certain angle of elevation l , the friction coefficient f between the known slope and the slider and the vertical load Q applied to the slider A (including the slider itself) weight).
Therefore, in order to make this slider A not self-locking during the ascending and descending process, the following two conditions must be met:
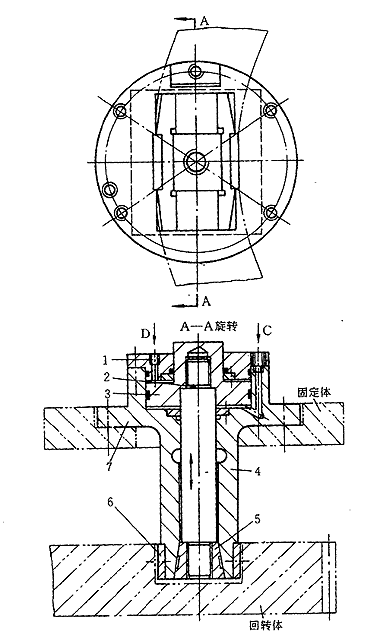
2 inclined floating clamping mechanismThe inclined floating clamping mechanism is shown in Figure 2. When the rotary table needs to be clamped and fixed, the pressure oil passes through the oil filter, the oil pump and the electromagnetic reversing valve, and then enters the oil chamber through the C port to push the piston to move. The inclined slider 5 on the piston shaft 2 is driven to move upward, and the elastic clamping body 4 is outwardly opened by a force larger than the force applied to the piston due to the action of the inclined surface, so that the clamping rail plate 6 is clamped. It is in contact with the clamping groove surface (annular groove opened on the rotary body) and is pressed to generate a pressure. Finally, the rotary table is reliably clamped by the frictional force F generated between the clamping rail plate 6 and the clamping groove surface. In order to make the clamping body smaller in volume and better in stress, the clamping body is generally symmetrically distributed on the turntable, and the arm is made larger as much as possible. We use four symmetrically arranged clamping bodies so that the central shaft is only subjected to torsional moments and the radial force is zero (Fig. 2), so that the turntable maintains high precision. When it is necessary to loosen, it is only necessary to pass a certain pressure oil to the D port, so that the piston moves downward, the ramp slider is driven to overcome the clamping resistance movement, and at the same time, due to the elasticity of the clamping elastic body 4, the clamping rail plate is clamped. Disengage from the clamping annular groove surface. In this example, the gap between the clamping rail plate and the annular groove surface of the rotating body is always maintained at about 0.1 mm (two sides) for the reliability and rapidity of the clamping action. As can be seen from the foregoing, in the bevel slider mechanism, the slider can be lifted and lowered freely while satisfying the conditions of l <( p /2)-Ø, l >Ø. Generally, we take a small coefficient of friction between the slider and the bevel, f = 0.10, then the friction angle Ø = tg -1 f = 5.246 °. In order to make the piston use a smaller driving force P, a larger clamping force Q is generated, only l > Ø, but considering the influence of other factors, here take l = 7 ° 30 ', it is clear that l + Ø<( p /2) is established to satisfy the slider self-locking condition. The clamping force Q required for the clamping body is 85 kN, and since P = Qtg ( l + Q), it is only necessary to make the driving force P generated by the piston about 20 kN to achieve clamping. Obviously, the P force is much smaller than the Q force. Compared with the conventional cylinder without clamping the slider (clamping), the cylinder volume is much smaller when the same oil pressure is required to produce the same clamping force. At the same time, the cost is low, no need for disc spring reset, saving space and making the whole mechanism smaller. Through the above analysis, it can be seen that the inclined floating clamping mechanism has many advantages compared with the traditional cylinder, and has certain generalization and practicability. For the engineering and technical personnel engaged in mechanical design, it provides a relatively novel one when doing such design work. The clamping mechanism for reference. | |||||||||||||||
Peach Shape Post,Garden Wire Mesh,Welded Garden Fence Panels,Curved Welded Wire
Anping Xinlong Wire Mesh Manufacture Co.,Ltd. , https://www.xinlongfence.com