Ammonia gas hazard:
Ammonia has corrosive and irritating effects on the contacted skin tissue, can absorb water in the skin tissue, denature the tissue protein, and saponify the tissue fat, destroying the cell membrane structure. Ammonia has a very high solubility, so it is mainly irritating and corrosive to the upper respiratory tract of animals or human bodies, and is often adsorbed on the skin and mucous membranes and conjunctiva, thereby causing irritation and inflammation. It can paralyze the respiratory cilia and damage the mucosal epithelial tissue, making pathogenic microorganisms easy to invade and weakening the body's resistance to disease. Ammonia is usually inhaled into the human body in the form of a gas. After being inhaled into the lungs, ammonia easily enters the bloodstream through the alveoli, and binds to hemoglobin, which destroys the oxygen transport function. The ammonia that enters the alveoli is neutralized by a small amount of carbon dioxide, and the rest is absorbed into the blood. A small amount of ammonia can be excreted with sweat, urine or breathing.
Short-term inhalation of a large amount of ammonia can cause tears, sore throat, hoarseness, cough, bloodshot, chest tightness, difficulty breathing, may be accompanied by dizziness, headache, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, etc., severe cases can occur pulmonary edema, adults Respiratory distress syndrome, and respiratory irritation may occur. If too much ammonia is inhaled, resulting in too high a concentration of ammonia in the blood, it will cause cardiac arrest and respiratory arrest through the reflection of the trigeminal nerve endings, endangering life.
Long-term exposure to ammonia, some people may have symptoms such as skin pigmentation or finger ulcers
Description of arsine gas:
Chemical formula AsH3. Colorless, garlic-like toxic gas; melting point -16.3 ° C, boiling point -55 ° C, density 2.695 g / liter; molecular structure is pyramidal. Acridine is slightly soluble in water;
Unstable, it is a strong reducing agent; it decomposes when heated to 300 °C. It is easy to burn to produce arsenic oxides and water when heated in air, and produces elemental arsenic and water when oxygen is supplied. Arsine can be obtained by reducing sodium arsenide, zinc arsenide or arsenic oxide with a metal in an acidic solution, or by hydrolyzing aluminum arsenide. Arsenic
Poison can cause vomiting and convulsions.
Hazardous hydrogen arsenic gas:
Mainly for varying degrees of acute hemolysis and kidney damage. The degree of poisoning is closely related to the concentration of inhaled arsine. The shorter the incubation period, the more severe the clinical manifestations.
Mild poisoning has dizziness, headache, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, joint and waist pain, mild yellow staining of the skin and sclera. Red blood cells and hemoglobin are reduced. The urine is soy sauce color, occult blood positive, protein positive, red and white blood cells. Blood urea nitrogen increased. May be associated with liver damage.
Severe poisoning has a sharp onset, including chills, high fever, coma, convulsions, convulsions, purpura, sclera, and severe yellow staining throughout the body. No urine or no urine. Anemia is aggravated, and reticulocytes are significantly increased. The urine is deep in color and the urine is strongly positive. Blood urea nitrogen is significantly increased, acute renal failure occurs, accompanied by liver damage. According to the history of occupational exposure, on-site investigation, the diagnosis of typical cases is not difficult. Early symptoms need to be differentiated from acute gastroenteritis and acute infection. After hemolysis occurs, it must be differentiated from hemolysis caused by other causes. In acute poisoning, especially in the early stage, urinary arsenic can be normal, early examination of urine routine, urinary bile, jaundice index, and reticulocyte, etc., to help diagnose.
Ethyl mercaptan gas hazard:
This product mainly acts on the central nervous system. Inhalation of low concentrations of vapor can cause headaches and nausea; higher concentrations of anesthesia. High concentrations can cause respiratory paralysis to death. Poisoning can cause vomiting, diarrhea, protein, casts and hematuria in the urine.

Concerned about surprises
Label: Harmfulness of ammonia, arsine gas, and ethanethiol gas
Previous: Double-effect evaporation process for the treatment of furfural wastewater Next: The principle of foaming machine
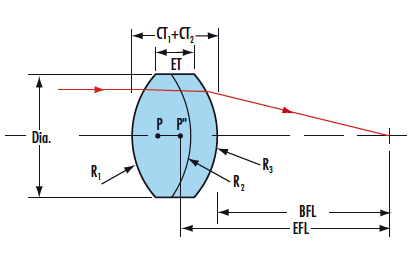
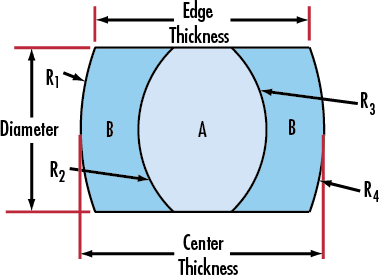
Achromat doublet lenses have significantly better optical performance than singlet lenses in visible imaging and laser beam manipulation applications.It consists of a positive low-index Crown Glass lens element cemented to a negative high-index Flint Glass lens element. The elements are chosen so as to cancel chromatic aberration at two well-separated wavelengths, usually in the blue and red region of the spectrum. Focal length is constant at those two wavelengths and focal length shifts are virtually eliminated across the visible wavelengths. One frequent use is to achieve diffraction limited focusing of a laser beam. Negative Achromat is typically used when there is a need to eliminate chromatic aberration. In addition to reducing chromatic aberration at the design wavelengths, spherical aberration and coma are greatly reduced. We always make our achromats as precise specifications and tolerances for uncompromising image quality upon customer's requirement.
Doublet Achromatic Lens Triplet Achromatic Lens
Specification of our achromatic lens as follow:
*Material:BK7,ZF2,ZF7(or according to your request)
*Dia.:+0/-0.05
*Center thickness tolerance:+/-0.1
*Surface quality: 60-40 Scrath/Dig
*Surface figure:0.5-0.2
*Centration < 3arc min
*Chamfer:0.1-0.25*45 degrees
*Design wavelength:486.1mm,587.6mm,656.3mm and upon request.
Achromatic Doublet Lens,Negative Optical Achromats Lens,Optical Achromatic Lens,Big Dimension Achromatic Lens
China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.opticsrealpoo.com
