1.1 austenitic stainless steel
Austenitic stainless steel was introduced in Germany in 1913. Austenitic stainless steel refers to stainless steel having an austenite structure at normal temperature. Classification: Fe-Cr-Ni (main body); Fe-Cr-Mn. When the steel contains about 18% Cr, 8%-10% Ni, and about 0.1% C, it has a stable austenite structure [1]. Austenitic chrome-nickel stainless steel includes the famous 18Cr-8Ni steel and high-Cr-Ni series steel which is developed by adding Cr, Ni content and adding elements such as Mo, Cu, Si, Nb and Ti. Austenitic stainless steel is non-magnetic and has high toughness and plasticity, but its strength is low. It is impossible to strengthen it by phase transformation. It can only be strengthened by cold working. For example, adding elements such as S, Ca, Se, Te has good Easy machinability.
1.2 Comparison of domestic and foreign austenitic stainless steel grades
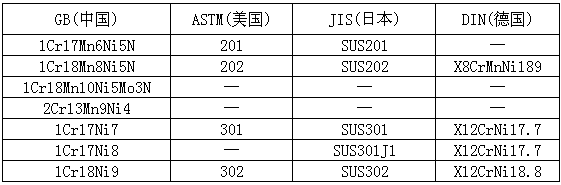
Table 1-2
1.3 316L austenitic stainless steel
When the steel contains about 18% Cr, Ni 8% to 10%, and C about 0.1%, it has a stable austenite structure. Austenitic chrome-nickel stainless steel includes the famous 18Cr-8Ni steel and high-Cr-Ni series steel which is developed by adding Cr, Ni content and adding elements such as Mo, Cu, Si, Nb and Ti. Austenitic stainless steel is non-magnetic and has high toughness and plasticity, but its strength is low, it is impossible to strengthen it by phase transformation, and it can only be strengthened by cold working. If S, Ca, Se, Te and other elements are added, it has good machinability. In addition to the corrosion resistance of oxidizing acid medium, such steel can also resist the corrosion of sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, formic acid, acetic acid, urea, etc. if it contains elements such as Mo and Cu. If the carbon content of such steel is less than 0.03% or contains Ti or Ni, the intergranular corrosion resistance can be remarkably improved. High silicon austenitic stainless steel concentrated nitric acid has good corrosion resistance [2].
Development and application of 1.4 316L austenitic stainless steel
316L stainless steel (00Cr17Ni14Mo2) belongs to the American 1970s AISI300 austenitic stainless steel series. It is a classic 18-8 (Cr-Ni) stainless steel modified alloy, which is a Cr-Ni-Mo ultra-low carbon stainless steel developed to improve corrosion resistance [3]. Good corrosion, heat resistance, low temperature strength and mechanical properties; good hot workability such as stamping and bending, no heat treatment hardening, no magnetism, used in household products (tableware, cabinets, boilers, water heaters), auto parts, Medical equipment, building materials, chemicals, food industry, ship parts. According to different requirements, its common heat treatment processes mainly include: solution treatment, stabilization treatment and stress relief treatment. Due to its wide application, the research of heat treatment process has a good guiding significance for production [4].
1.5 heat treatment of austenitic stainless steel
1.5.1 Solution treatment of austenitic stainless steel
The purpose of solution treatment is to improve the corrosion resistance and resistance of intergranular corrosion of stainless steel. Since the austenitic stainless steel does not undergo a phase change during the heat treatment, the solution treatment is to heat the austenitic stainless steel to 1050 ° C -1100 ° C, so that the carbide containing alloying elements is dissolved into the austenite solid solution to become a single phase. The super-saturated solid solution maintains the single-phase austenite structure obtained at a high temperature to room temperature after rapid cooling. The traditional process is to cool the forgings with a final forging temperature of 900 °C - 950 °C to room temperature, and then reheat to 1000 °C - 1050 °C for solid energy. In order to change this irrational process, the use of forging waste heat for solution treatment is used to improve labor efficiency and at the same time reduce energy consumption. After repeated trials, it was finally determined that the forging heat treatment solution was used: Immediately after forging, the furnace was heated up to 1050 °C, and the temperature was cooled to room temperature according to the effective section of the forging for 40 min. Forgings should be completely submerged in water, circulated with water, and the water temperature should not exceed 60 °C. In the process of water cooling, always pay attention to the water temperature, and use the low temperature thermometer to measure the water temperature in time.
1.5.2 Aging treatment of austenitic stainless steel
Refers to a metal or alloy workpiece (such as low carbon steel) after solution treatment, after high temperature quenching or after a certain degree of cold working deformation, at a higher temperature or room temperature to maintain its performance, shape, size change with time of heat treatment Process. Generally speaking, after aging, the hardness and strength are increased, and the plastic toughness and internal stress are reduced. Steel with a higher carbon content obtains a high hardness immediately after quenching, but its plasticity becomes very low. After the quenching of the aluminum alloy, the strength or hardness does not immediately reach the peak, and the plasticity does not decrease, but instead increases. After a long period of time (for example, 4-6 nights and nights), the strength and hardness of the quenched alloy are significantly increased, while the plasticity is decreased. The strength and hardness of such a quenched alloy change significantly with time, which is called aging. The aging effect at room temperature is called natural aging, and the aging at a certain temperature is called artificial aging. Aging treatment is a process in which materials are consciously stored at room temperature or at a higher temperature for a longer period of time to cause aging. The artificial aging treatment used in this experiment.
Related information recommended:
Solid solution and aging of stainless steel - overview (1)
Solid solution and aging of stainless steel - testing equipment (2)
Solid solution and aging of stainless steel - process flow (3)
Solid solution and aging of stainless steel - test data and phase diagram (4)
Soap Holder,Shower Soap Holder,Bathroom Basket,soap dish,stainless steel soap rack,etc
WELL DESIGN: Cambered surface Slotted design soap dish, Self Draining, Stylish and functional, Porous design lift to air drying faster
DURABLE CONSTRUCTION: Soap case holder made from 304 stainless steel, get best care to your skin
STYLISH MODERN: Let your bathroom become more simple and upscale!Applicable to families, hotels, home stay and other places to use.
bathroom basket,bathroom rack,bathroom shelves,shower rack,storage basket
Shenzhen Lanejoy Technology Co.,LTD , https://www.baking-rack.com
